Borescopes: Definition, Working Principles and Industrial Applications
Release time:2025-08-05 Click:803
A borescope, commonly known as an industrial borescope, is a specialized inspection tool integrating precision optical or electronic imaging systems. Its core function lies in penetrating narrow entrances or complex internal structures through an elongated flexible or rigid probe, transmitting real-time images of areas inaccessible to the naked eye to the operator. This enables visual non-destructive testing (NDT) of enclosed spaces.
Core Structural Principles and Technical Parameters
A standard borescope consists of the following core subsystems, whose performance directly impacts inspection accuracy and reliability:
1.Insertion tube probe: Miniaturized optical pathway carrier
Rigid probe: Metal hard-tube structure (typically stainless steel), offering high optical stability. Suitable for linear channel inspection;
Flexible probe: Multi-joint steering mechanism (≥4 directions) with high-toughness coating, bending angle ≥160°, adaptable to complex bends.

2.Imaging System: Core for image capture and transmission
Optical lens assembly: High-resolution gradient index lens array for lossless image transmission.
Electronic imaging: Front-end micro CMOS/CCD image sensor (typically 160k–2MP).
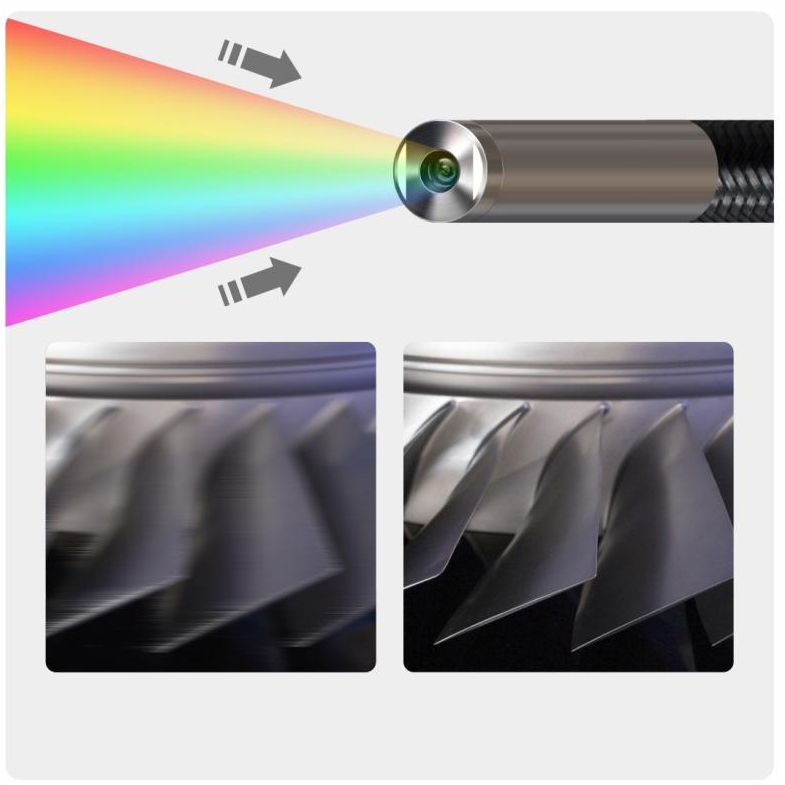
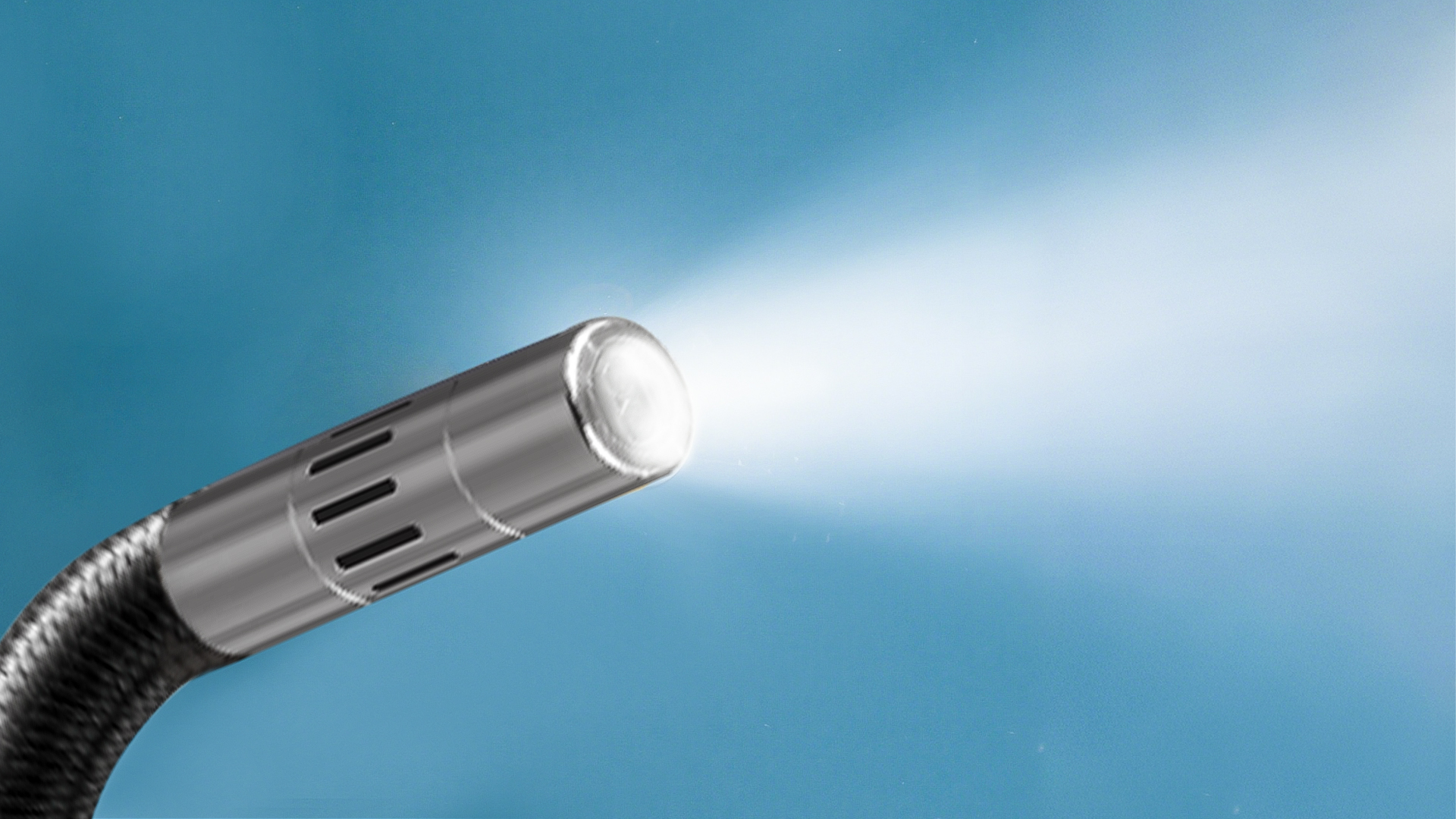
3.Illumination System: Ambient light compensation module
High-brightness LED array (often ≥6 units), color temperature 5600–6000K, max illuminance 18,000LX.
Fiber-optic light guide technology (for ultra-fine diameter probes).

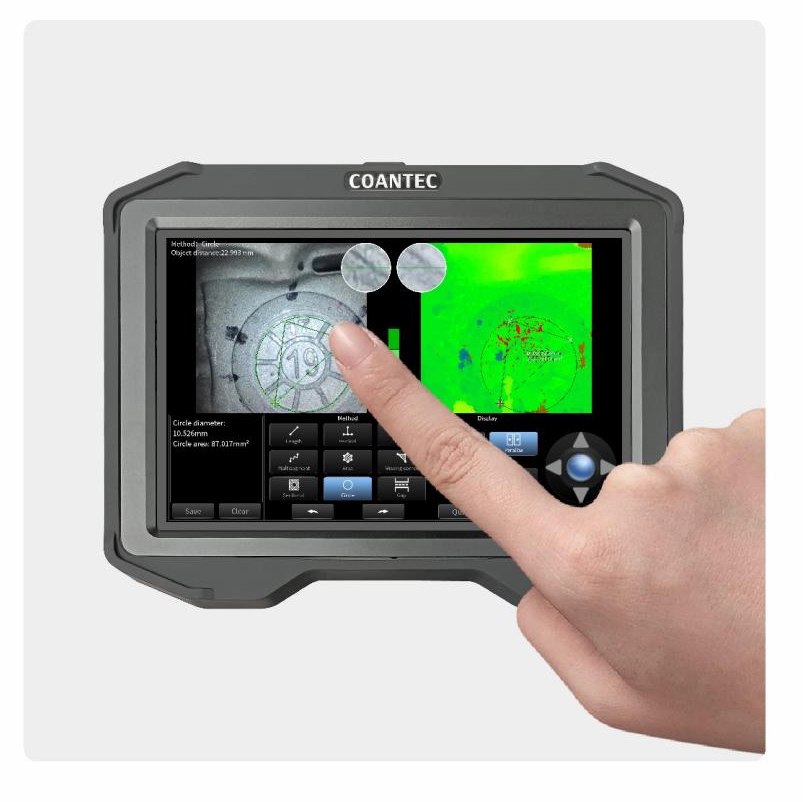
4.Control Unit: Human-machine interface and data processing terminal
HD LCD display (5.5–8 inches), standard resolutions: 1280×720, 1920×1080.
Video recording system (supports 1080P video & JPEG capture).
WiFi/Bluetooth data transmission module.

Key Performance Parameters:
Probe diameter: Φ0.95mm – Φ8mm (directly determines application scope).
Working length: 1m – 20m+ (custom lengths available).
Depth of field: 5–100mm (varies by camera solution).
Waterproof rating: IP67 (30-min protection at 1m depth).
Core Industrial Value & Applications
Borescope technology enables non-destructive internal visualization, providing critical inspection solutions for modern industries:
Aero engines: Turbine blade ablation inspection, compressor foreign object detection.
Energy/Power: Boiler pipe corrosion assessment, turbine rotor dovetail groove crack inspection.
Automotive: Cylinder block casting defect identification, transmission assembly verification.
Precision Machinery: Internal burr detection in complex workpieces, hydraulic valve block cleanliness validation.
Infrastructure: Bridge cable corrosion evaluation, pipeline weld quality inspection.
Technology Evolution Trends
Depth-visual fusion.
AI-powered defect recognition.
Submillimeter 3D point cloud reconstruction (<0.1mm accuracy).
Extended Guidance:
When selecting a borescope system, prioritize evaluation of ambient temperature (high-temperature models withstand 300°C), explosion-proof certification, and measurement precision to ensure optimal alignment with inspection requirements.
As a cornerstone of modern NDT systems, the continuous innovation in borescope technology is expanding the boundaries of industrial visualization. It delivers indispensable support for predictive maintenance and quality control across critical sectors.
Hot products

Industrial borescope 3D measurement function - X5 Series

Engine borescope inspection camera Industrial Videoscope- C68 series
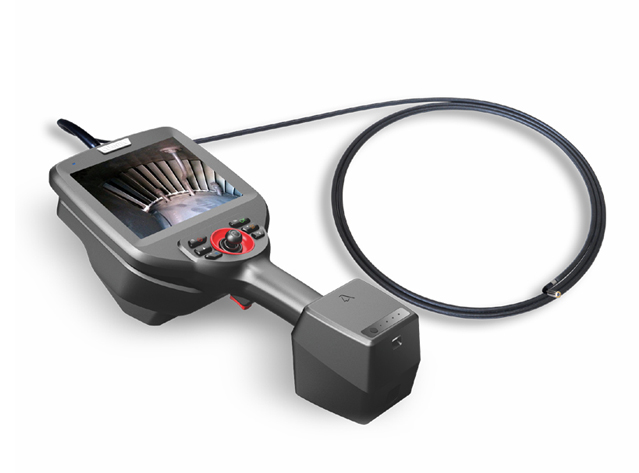

Coantec C65 series 3D Measurement High Definition Industrial Videoscope
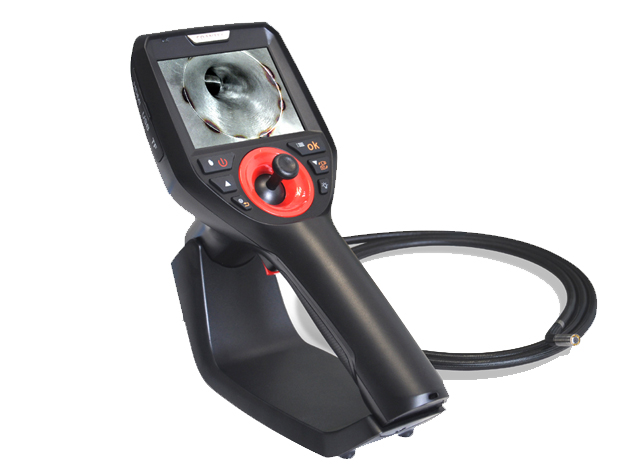

Super HD Mega Pixel Industrial Videoscope of Coantec C40 series
Tel:+86 13714520051
E-mail:flora@chinavideoscope.com
